Part of running a business is making sure your employees and customers are taken care of. But what happens when there are accidents involving a customer or someone you employ? When an accident occurs, you not only have to worry about the safety of those involved but the safety of your business as well. With an increasing number of businesses facing lawsuits, it is important to protect yourself against any liability. The following is important information about liability and how you can protect the business you have worked hard to build.
What is Business Liability?
A business has a duty to maintain safe premises and operations. Liability occurs when a business’s negligence causes injury to others. Negligence could arise from a business’s operations, its employee’s conduct, or even its advertising.
Of course, injuries can be the result of someone else’s negligence, which would mean the business is not responsible. Many businesses will still become the targets of lawsuits after an accident or injury in the hopes of getting any money at all. An attorney can advise you about whether you are liable in certain situations and what your next steps should be.
What Situations Result in Liability for Businesses?
There are many situations that could pose a liability risk for a business. Even everyday business activities could turn into a liability risk. Some common situations that pose a liability risk are:
- Car accident involving a company vehicle.If an employee driving a company vehicle is involved in a car accident, any liability falls on the company. If the vehicle is covered by a commercial vehicle insurance policy, then your insurance company will work with the other parties and their insurance companies. Of course, many drivers may still choose to sue the business. Some insurance policies will take care of defending you from lawsuits as well.
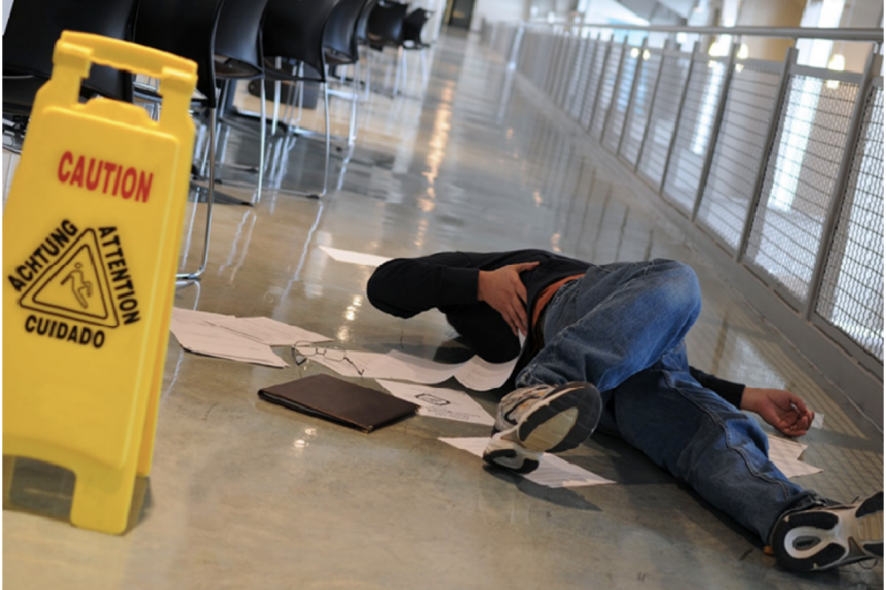
- Injuries on business property. Businesses owe a duty of care to people on its property to make sure conditions are safe and to warn customers or others about potentially unsafe conditions. If a customer is injured because of a dangerous condition on company property, you may be subject to premises liability. For example, if someone slipped and fell on water on the floor and there was no wet floor sign, this could spell trouble for your company.
- Employee injuries. Some businesses involve naturally dangerous operations or conditions, such as construction or warehouses. Even slippery floors could pose a risk of injury to employees. If an employee is injured at work, the company may be liable if the company’s negligence played a role. If an employee is injured, he or she may claim compensation through a business’s workers’ compensation insurance policy or may choose to sue the employer directly.
- Products liability. If you manufacture or sell products to customers, trouble can arise if a customer is injured by your product. Say you sell food, and a customer gets food poisoning. Or you might sell a defective product that injures someone. Products liability is often a form of strict liability, meaning that you will be automatically liable for any injuries caused by defective products. A robust insurance policy can protect you in this situation.
- Slander, libel, or copyright infringement. Advertising is a great marketing tool for any business. But sometimes, people can get aggressive with their marketing tactics and run into trouble. Commercials or ads that competitors or others view as disparaging against them could spur claims of slander or libel. Your business’s logo may also face copyright infringement claims if another business thinks your logo looks too much like theirs.
What Steps Should You Take to Protect Your Business?
Maintain safe conditions and practices.
Making sure your business is a safe environment and that all employees act in a prudent manner is the first defense against liability. Take special care to prevent unsafe conditions, such as placing no slip mats on floors. If an unsafe condition is brought to your attention, fix it as quickly as possible and warn customers with appropriate signs and warnings. If your company uses drivers in its business, make sure to check driving records before hiring anyone and speak to your employers about maintaining safe practices during their shifts. Pre-employment safety training can go a long way in preventing accidents and hazards.
Acquire business liability insurance.
Having a liability insurance policy is one of the best things you can do to protect your business. There are many different types of insurance policies for businesses, all with differing levels of coverage. A general liability policy will cover you for any lawsuits against your company. Commercial auto insurance will cover any accidents involving company vehicles, including any injuries. Workers’ compensation insurance will provide coverage for any employees who are injured on the job.
Consult a business liability attorney.
Even if you take all the right precautions, you can still face liability. Sometimes, people choose not to take benefits from an insurance company and decide to sue the company instead, hoping to get more money. It is a good idea to consult an attorn
ey who can help you protect your business. A good attorney can tell you whether you are liable in certain situations and help you defend against any lawsuits. It is also a good idea to consult with an attorney before you start a business to make sure that you minimize any risks and that you do all that you can to protect yourself while you operate your business.
About the Author
 †Christian Denmon is a trial lawyer at Denmon Pearlman, a Tampa Injury LawFirm specializing in representing victims of personal injury. He has been recognized as one of the “Top 100” trial lawyers in Florida, and the firm has a reputation for taking on insurance companies all over the state.
†Christian Denmon is a trial lawyer at Denmon Pearlman, a Tampa Injury LawFirm specializing in representing victims of personal injury. He has been recognized as one of the “Top 100” trial lawyers in Florida, and the firm has a reputation for taking on insurance companies all over the state.
Read Next: